Types of Sterile Packaging
Cleanliness is essential to the success of any healthcare treatment. When medical environments and devices are not clean, the patient is at greater risk for infections and complications.
Medical devices stored improperly can become contaminated with bacteria, viruses, or other harmful substances. If contaminated devices are used on a patient, they can cause healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) or surgical site infections (SSIs).
According to the CDC, SSIs cause prolonged hospitalizations, unplanned readmissions, and even death. The CDC also reports that nearly half of the estimated 157,500 SSIs could have been prevented with evidence-based strategies, such as using proper sterile packaging and procedures.
Sterile packaging protects the patient by keeping medical devices safe for use. They use specific materials and methods to maintain sterility and integrity.
What is Sterile Packaging?
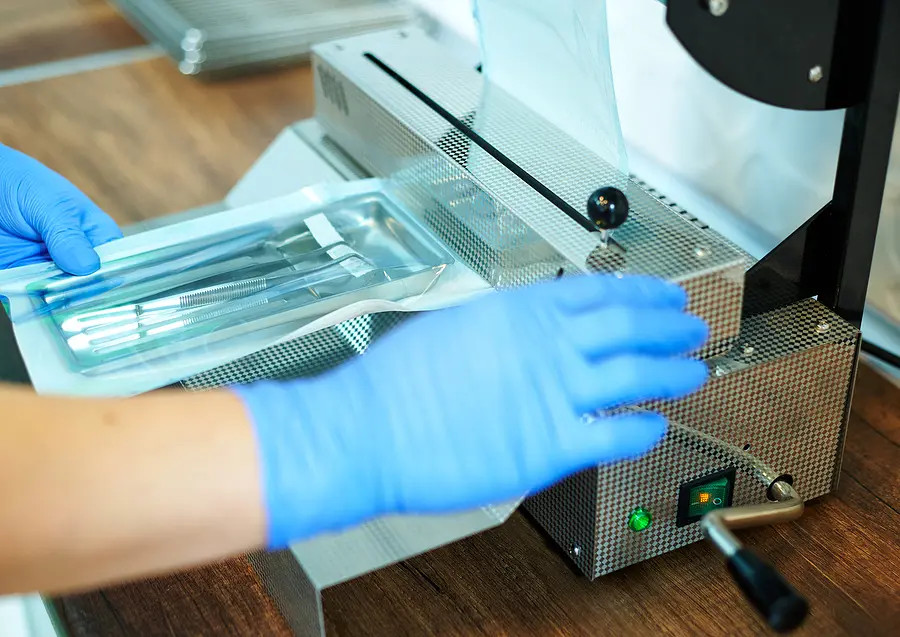

Sterile packaging provides a barrier against microbes and bacteria for medical devices that have been sterilized for reuse. The sterile packaging process involves a selection of appropriate materials, sterilization techniques, and quality control measures to maintain high standards of sterility. You should consider packaging carefully; accounting for usability aspects, easy product identification, label readability, and aseptic presentation.
Types of Sterile Packaging
There are three main types of sterile packaging. Each serves a particular purpose aimed at protecting and maintaining the function of the medical device.
Primary Packaging
Primary packaging is the barrier in direct contact with or closest to the medical device. This layer is made of impermeable materials such as paper, plastic, or metal.
Secondary Packaging
Secondary packaging is a durable layer surrounding the primary packaging. It is typically a strong material, such as cardboard or plastic.
Primary and secondary packaging are for maintaining sterility while also preventing physical damage to the device. Multiple layers prevent breakage even if the primary packaging fails.
Tertiary Packaging
Tertiary packaging is for storage and transportation. It consists of of corrosion-resistant materials, such as plastic or metal. This layer allows for safe storage and protects the device from damage.
Select your sterile packaging based on the specific needs of each medical device. You should carefully consider the requirements for temperature and humidity conditions.
Sterile Packaging Materials & Designs
There are many sterile packaging materials and designs to choose from. Materials need to be compatible with the sterilization process, protect against contamination, provide a barrier to microbial penetration, and maintain sterility of the device post-sterilization.
Commonly used materials include:
- Medical-grade paper – Used for primary packaging, often as pouches or wraps. It is permeable to sterilizing agents, but impermeable to microorganisms.
- Plastic – Used for primary packaging, often as blister packs, trays, or clamshells. Plastic protects devices from moisture, gasses, and contaminants. Types of plastics used include polyethylene, polypropylene, and polyvinyl chloride (PVC).
- Cardboard – Used for secondary packaging, often as cartons or boxes. Cardboard provides structural support and helps maintain the integrity of inner layers.
- Adhesive Tape – Tape helps secure sterile packaging, serving as a seal or wrap. Tape provides a tight closure and prevents the entry of contaminants.
- The design of sterile packaging can also vary based on the needs of your devices. Popular types of sterile packaging designs include:
- Sterilization pouches – A sterilization pouch or peel pack, is a disposable package that you can use in a sterilizer. The design allows for effective sterilization, but also safe handling and storage by maintaining sterility after processing. Peelable packs also facilitate proper aseptic presentation, meeting all requirements of the FDA.
- Tyvek® pouches – Tyvek pouches are sterilization pouches made of nonwoven material containing high-density polyethylene fibers.
- Thermoform trays – Thermoform or vacuum-formed trays come in various shapes, sizes, and configurations. They provide a customized, secure positioning for devices in a sealed tray.
- Clamshell packaging – Clamshell packaging consists of clear plastic containers with hinges. They offer protection and visibility.
- Tray and lid systems – These systems organize multiple devices within a sterilized tray. They are made of durable materials, usually plastic or metal, to provide protection.
Sterile Packaging Methods
After selecting the sterile materials and designs, you will need to decide on the most effective packaging method to seal your devices. You should consider the type of medical device, materials, packaging, regulatory requirements, and desired sterility when choosing your method.
Here are two of the most common methods:
- Heat sealing – Heat sealing uses heat and pressure to melt the packaging material to create a seal. Heat sealing is typically for pouches or wraps and is an effective method for keeping out contaminants.
- Induction sealing – Induction sealing uses an electromagnetic field to generate heat and create an airtight seal. Induction sealing is typically on containers with metal or aluminum foil seals.
After the sterile packing process is complete, your devices are ready for sterilization. You should select the most effective sterilization technique to eliminate microorganisms and maintain the sterility of your packaged devices.
Maintain Clean and Healthy Medical Environments with Medical Waste Pros
Medical Waste Pros partners with medical waste experts nationwide. Our partners focus on maintaining safe and healthy environments for all kinds of healthcare facilities and businesses. Give us a call at (888) 755-6370 to learn more about our services and to connect with providers near you. We look forward to assisting you in all aspects of medical waste management.










