What are the OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens Training Requirements?
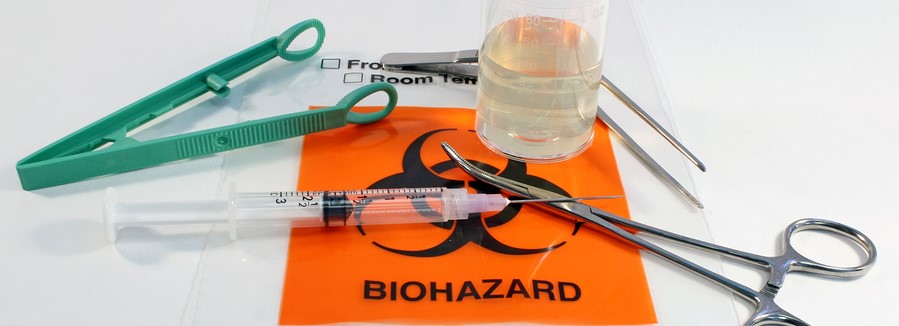
OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens Training is critical for employees who risk exposure to blood and other potentially infectious materials (OPIMs) in the workplace. Training enables employees to protect themselves, prevents exposure incidents in the workplace, and fulfills OSHA’s Bloodborne Pathogens standard requirements.
Learn more in the video and transcript below about who needs OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens training, what the training covers, and your options for providing training for your employees.
Video Transcription
What is the OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens Standard?
As amended by the Needlestick Safety and Prevention Act of 2000, OSHA’s Bloodborne Pathogens standard requires a range of different safeguards to protect employees from exposure to infectious materials.
The Bloodborne Pathogens standard is designed to protect from exposure risks including:
- Blood, body fluids, and other OPIMs
- Unfixed human tissues/organs
- Organ cultures
- HIV-containing cell/tissue cultures
- HIV- or HBV-containing culture media
Healthcare Employees Covered by the Bloodborne Pathogens Standard
Although according to OSHA the Bloodborne Pathogens standard applies to all employees who are potentially at risk of exposure to blood and OPIMS in the workplace, some common examples include:
- Physicians, nurses, surgeons, etc.
- Medical researchers
- Dentists and dental assistants
- Pharmacists and pharmacy technicians
- Police and paramedics
- Tattoo artists
- Sports coaches
Training Programs for the Bloodborne Pathogens Standard
At its core, the goal of the bloodborne pathogen training program is to help protect workers like nurses and paramedics from occupational exposure to blood and OPIMs.
Bloodborne pathogen awareness training programs cover things like exposure response plans and safety requirements for minimizing potential future exposures. No matter if employees have done it before or are being trained for the first time, they all are required to be trained annually.
Topics to Cover During Bloodborne Pathogens Training
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)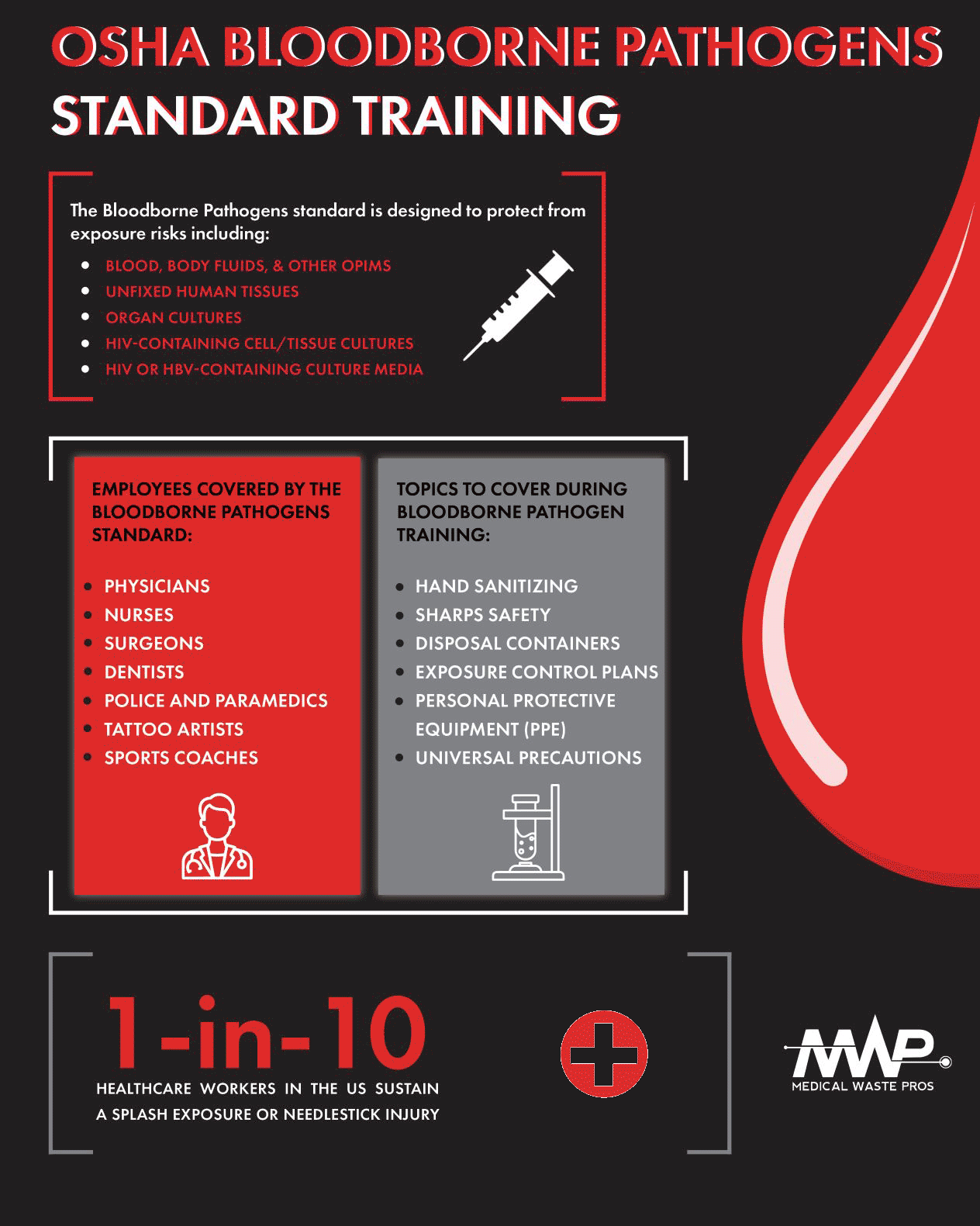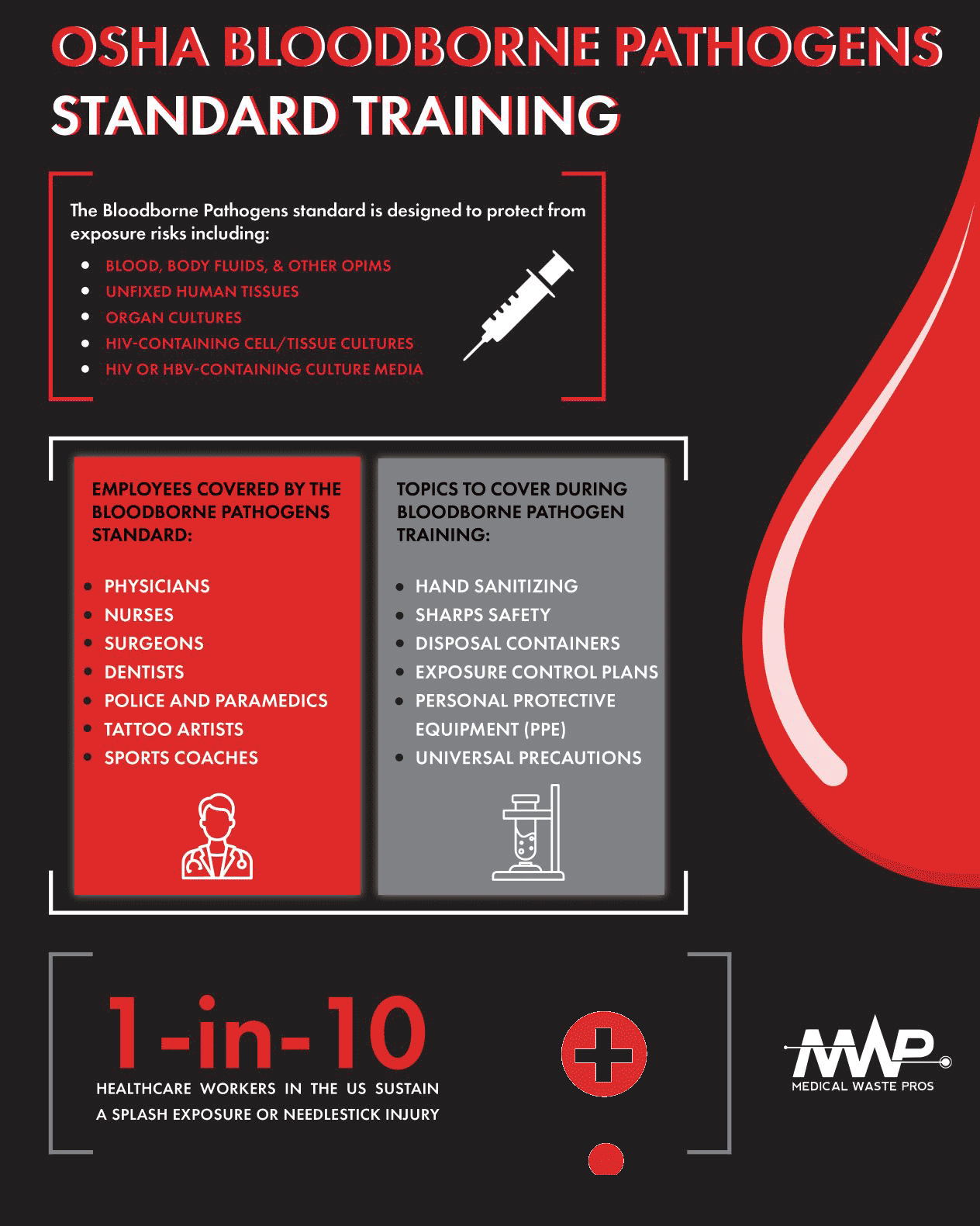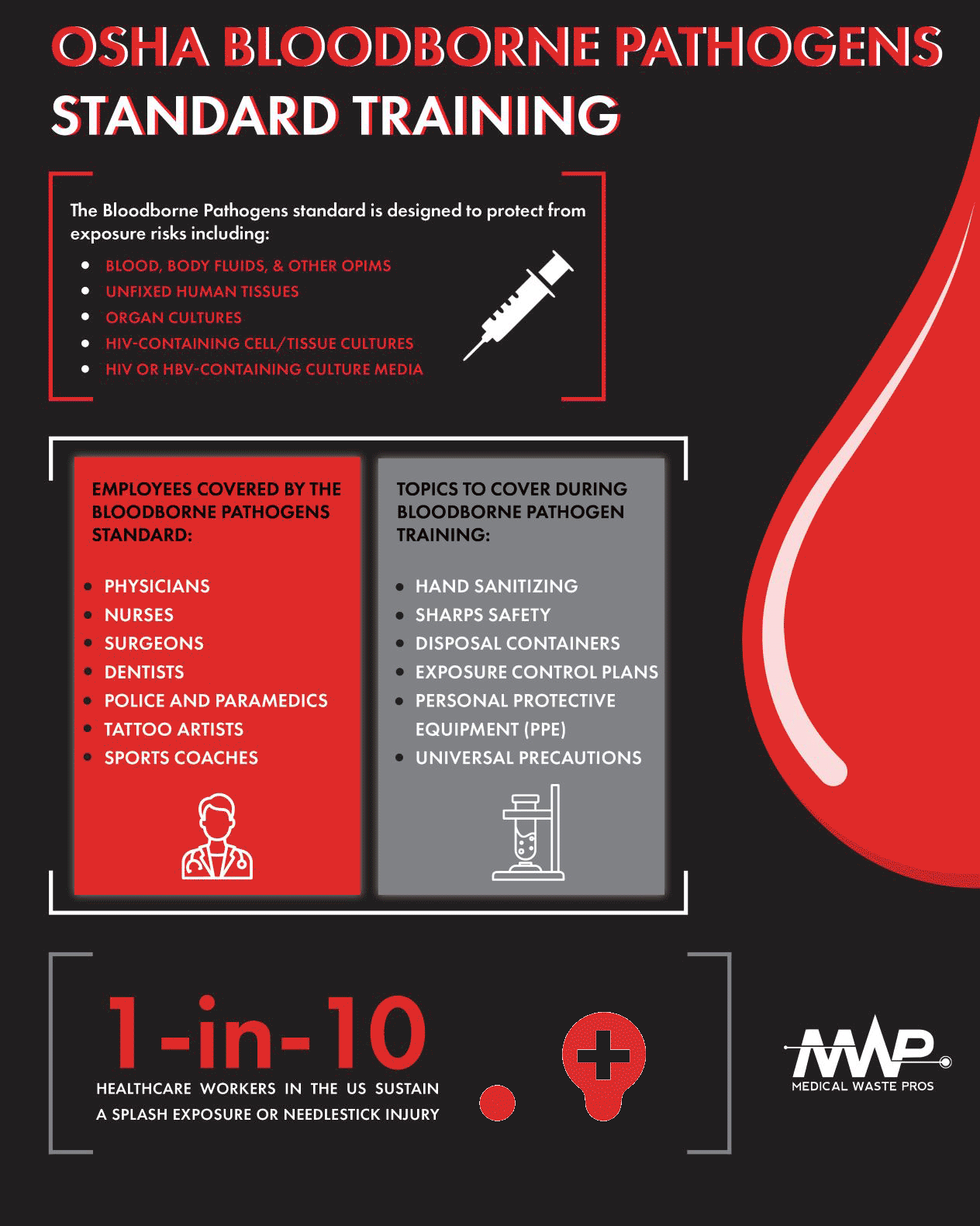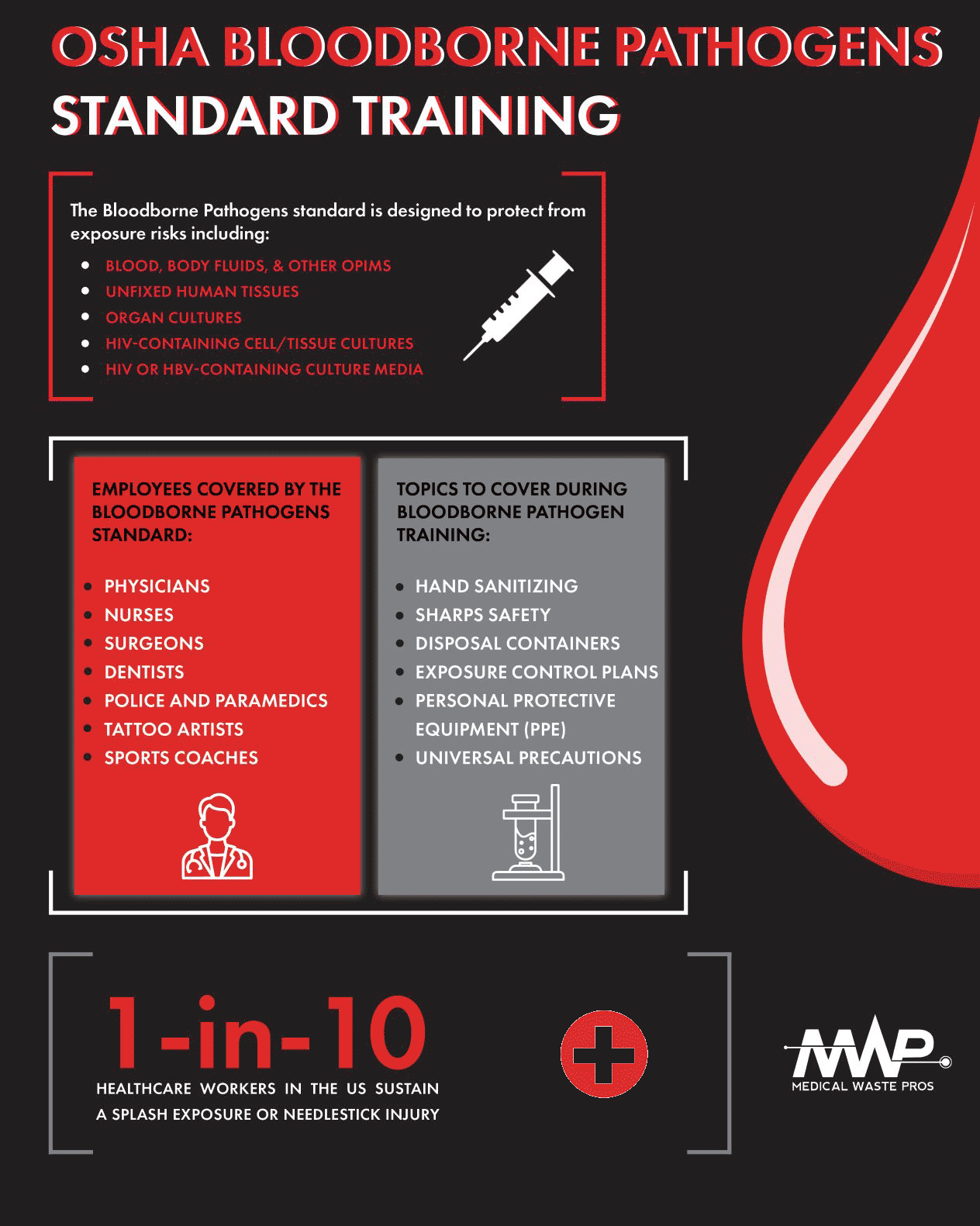
The OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens standard requires the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) whenever there is reasonable anticipation of exposure to blood or OPIMs.
Various types of PPE are used to protect against the transmission of germs through different contact and droplet routes. Some of the most common types of PPE needed in the workplace include:
- Latex, rubber, or nitrile gloves
- Protective goggles/glasses
- Face shields
- Surgical masks
- Aprons/gowns
- Head/shoe covers
Hand Sanitizing
One of the easiest ways for potential health hazards to spread is through poor hand hygiene, making it essential to ensure employees follow proper hand-washing techniques.
Recommendations for washing hands include vigorously scrubbing with soap and water for 40-60 seconds, and 20-30 seconds using an alcohol-based cleaning product. Moreover, hand sanitizing is especially important in situations like:
- After removing PPE
- After contact with blood or OPIMs
- Before or after patient care
Universal Precautions (UP)
Universal Precautions (UP) were originally recommended by the CDC in the 1980s as a way to protect employees from HIV, HBV, and other bloodborne pathogens in human blood, body fluids, and OPIMs.
UP is an approach to infection control where all human blood and potentially infectious materials are treated as if they are known to be infectious regardless of a patient’s infections and health status.
Sharps Safety
The Needlestick Safety and Prevention Act was passed in 2000 and specifically outlines safe practices for handling sharps since accidental sharp injuries are one of the most common exposure risks.
Types of sharps most frequently found in the workplace include:
- Needles
- Syringes
- Scalpels
- Lancets
When disposing of sharps, you need to collect them in a closable, puncture-resistant, leak-proof, and properly labeled/color-coded sharps container.
Exposure Control Plans
Although training drastically reduces the chances, accidental exposures to bloodborne pathogens are still a reality and something to plan for.
If blood or other OPIMs come into contact with the eyes, nose, or mouth or if there is parenteral contact (needlestick injury, cut, abrasion, bite), steps need to be taken immediately afterward to prevent any further impact.
Topics to cover in an exposure control plan include:
- Immediately washing needlestick injuries and cuts with soap and water
- Irrigating eyes with clean water, saline, or sterile irrigates
- Flushing splashes of water into the eyes, nose, and mouth
- Reporting exposures to a supervisor or instructor
- Seeking medical evaluation immediately after exposure so they can be treated as soon as possible
Disposal Containers/Bags
When it comes to transferring or disposing of regulated wastes like blood or other OPIMs, OSHA requires using containers that meet specific standards including:
- Closeable
- Color-coded red
- Labeled as biohazard (including biohazard symbol)
- Leak-proof during handling, storage, and transport
How Bloodborne Pathogen Training Programs Work
- Firstly, decide the best way to conduct training for employees. You can schedule a date for in-person training, or instead self-paced online training lets employees do it on their own schedule.
- If you opt for in-person training, a trained compliance officer will conduct bloodborne pathogen awareness training for all employees on the scheduled date. If you decide to go with an online training option, a self-paced system can be rolled out for employees to conduct training on their own time.
- Lastly, after bloodborne pathogen training is complete, you will get a training certificate to prove that annual training requirements are met.
Keep in Compliance with Services from Medical Waste Pros
Join numerous employers in a range of industries who we’ve helped to find solutions for ensuring they stay compliant with the OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens standard when you visit us at Medical Waste Pros today.
Fill out the form or give us a call at (888) 755-6370. We will connect you with a compliant medical waste disposal provider.










